[RxJava] Oper - ConbineLatest
ConbindLatest는 operators의 하나로 두개 혹은 그 이상의 Observable의 값이 모두 들어온 방출된 경우에 각 방출된 최신의 항목을 지정된 함수를 통해 결합하여 결과를 내 보낸다.
단 이때, 모든 Observable에게서 항목이 방출되어야 함수를 실행하여 결과를 내보내게 된다.
이는 이메일 혹은 비밀번호 및 전화번호를 입력받을 때 활용활 수 있다. 예를 들어 회원가입을 하게 되는 경우 이메일, 전화번호, 비밀번호, 비밀번호 확인의 각각을 체크하고 모두 방출된 경우에만 버튼을 활성화 하는 경우에 사용하기 좋다.
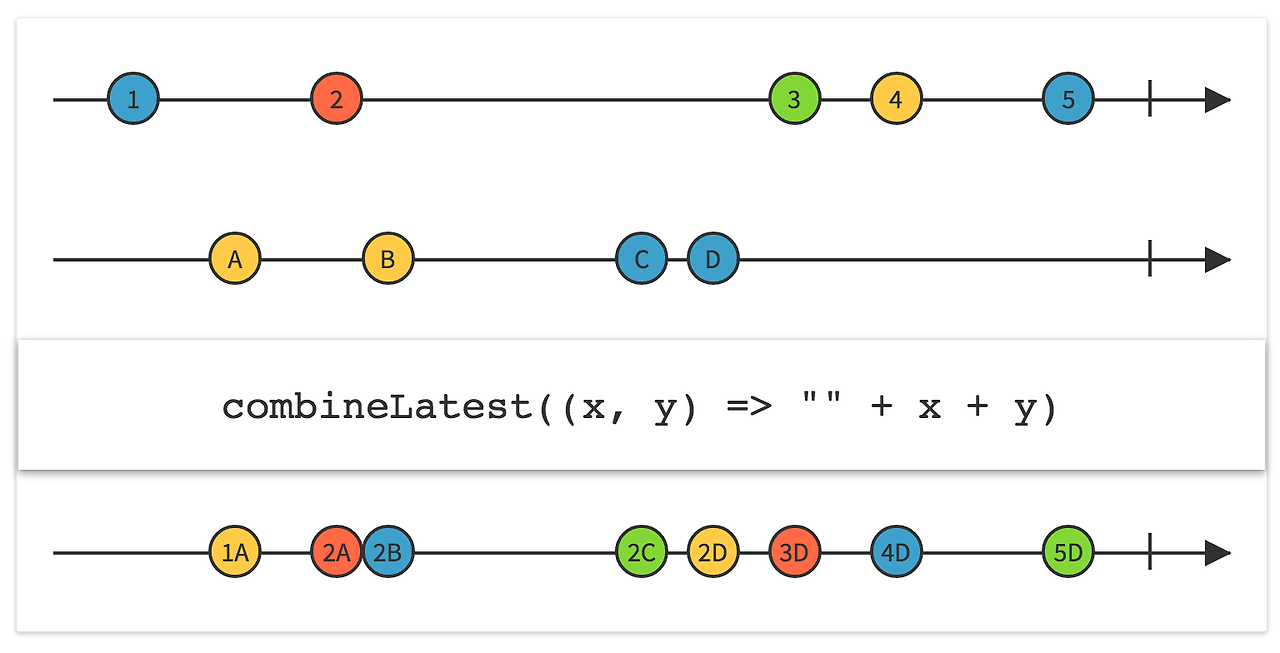
다음은 사용방법의 여러 가지 예이다.
Example 1
public static <T, S> Observable<Map<T, S>> zipMaps(final Map<T, Observable<S>> tasks) {
Objects.requireNonNull(tasks, "tasks is null");
return Observable.combineLatest(
tasks.entrySet()
.stream()
.map(entry -> Observable.combineLatest(
Observable.just(entry.getKey()),
entry.getValue(),
Pair::with))
.collect(ImmutableList.toImmutableList()),
xs -> Arrays.stream(xs)
.map(x -> (Pair<T, S>)x)
.collect(ImmutableMap.toImmutableMap(Pair::getValue0, Pair::getValue1)));
}
Example 2
private Observable<ProductDetail> getProductWithShoppingCartInfo(int productId) {
List<Observable<?>> observables =
Arrays.asList(backendApi.getProduct(productId), shoppingCart.itemsInShoppingCart());
return Observable.combineLatest(observables, objects -> {
Product product = (Product) objects[0];
List<Product> productsInShoppingCart = (List<Product>) objects[1];
boolean inShoppingCart = false;
for (Product p : productsInShoppingCart) {
if (p.getId() == productId) {
inShoppingCart = true;
break;
}
}
return new ProductDetail(product, inShoppingCart);
});
}
Example 3
private Observable<ProductDetail> getProductWithShoppingCartInfo(int productId) {
List<Observable<?>> observables =
Arrays.asList(backendApi.getProduct(productId), shoppingCart.itemsInShoppingCart());
return Observable.combineLatest(observables, objects -> {
Product product = (Product) objects[0];
List<Product> productsInShoppingCart = (List<Product>) objects[1];
boolean inShoppingCart = false;
for (Product p : productsInShoppingCart) {
if (p.getId() == productId) {
inShoppingCart = true;
break;
}
}
return new ProductDetail(product, inShoppingCart);
});
}
Example 4
public RxCommand<String> captchaCommand() {
if (_captchaCommand == null) {
Observable<Boolean> enabled = Observable.combineLatest(
_phoneNumberValid,
countdownCommand().executing(),
(valid, executing) -> valid && !executing);
_captchaCommand = RxCommand.create(enabled, o -> {
String phone = phoneNumber.value().toString();
Timber.i("fetch captcha with %s", phone);
Observable<String> fetchCode = fetchCaptcha(phone);
Observable<String> countdown = Observable.defer(() -> countdownCommand().execute(null).ignoreElements().toObservable()) ;
return Observable.concat(fetchCode, countdown);
});
}
return _captchaCommand;
}
Example 5
public RxCommand<Boolean> loginCommand() {
if (_loginCommand == null) {
Observable<Boolean> loginInputValid = Observable.combineLatest(
_captchaValid,
_phoneNumberValid,
(captchaValid, phoneValid) -> captchaValid && phoneValid);
_loginCommand = RxCommand.create(loginInputValid, o -> {
String phone = this.phoneNumber.value().toString();
String captcha = this.captcha.value().toString();
return login(phone, captcha);
});
}
return _loginCommand;
}