[안드로이드] SurfaceView
일반 View는 onDraw 메소드를 시스템에서 자동으로 호출해줌으로써 화면을 그린다. 그래서 화면에 늦게 그려질 수도 있다.
SurfaceView는 그리기를 시스템에 맡기는 것이 아니라 스레드를 이용해 강제로 화면에 그림으로써 원하는 시점에 바로 화면에 그릴 수 있다.
그래서 SurfaceView는 애니메이션이나 동영상과 같이 연산처리가 많이 필요한 뷰를 위해 사용된다.
SurfaceView는 더블 버퍼링 기법을 이용하여 SurfaceHolder가 Surface에 미리 그리고 이 Surface가 SurfaceView에 반영되는 방식이다.
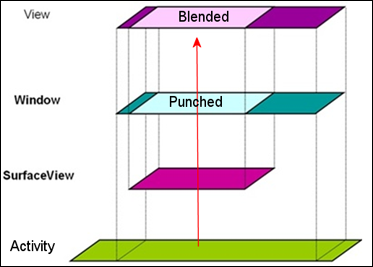
SurfaceView는 자기 영역 부분의 Window를 뚫어서(punch) 자신이 보여지게끔 하고 Window와 View가 블렌딩되어 화면에 보여지게 된다.
예제 코드
public class MySurfaceView extends SurfaceView implements SurfaceHolder.Callback {
Context mContext;
SurfaceHolder mHolder;
RenderingThread mRThread;
public MySurfaceView(Context context) {
super(context);
mContext = context;
mHolder = getHolder();
mHolder.addCallback(this);
mRThread = new MySurfaceView.RenderingThread();
}
@Override
public void surfaceCreated(SurfaceHolder surfaceHolder) {
// Surface가 만들어질 때 호출됨
mRThread.start();
}
@Override
public void surfaceChanged(SurfaceHolder surfaceHolder, int format, int width, int height) {
// Surface가 변경될 때 호출됨
}
@Override
public void surfaceDestroyed(SurfaceHolder surfaceHolder) {
// Surface가 종료될 때 호출됨
try {
mRThread.join();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
class RenderingThread extends Thread {
Bitmap img_android;
public RenderingThread() {
Log.d("RenderingThread", "RenderingThread()");
img_android = BitmapFactory.decodeResource(mContext.getResources(), R.drawable.android);
}
public void run() {
Log.d("RenderingThread", "run()");
Canvas canvas = null;
while (true) {
//canvas lock을 통해서 해당 캔버스에 draw가 들어와도 그리지 않는다.
canvas = mHolder.lockCanvas();
try {
synchronized (mHolder) {
canvas.drawBitmap(img_android, 0, 0, null);
}
} finally {
if (canvas == null) return;
//여기서 lock된 draw들을 그린다.
mHolder.unlockCanvasAndPost(canvas);
}
}
}
} // RenderingThread
[출처] [Android] SurfaceView 개념 및 예제|작성자 발그레환이