[머신러닝] Linear Regression 1
Linear Regression(수업방식)
간단한 예제를 통해 Linear Regression 을 알아본다.
1. Training Data Set
ML에 입력으로 사용될 데이터를
Numpy의ndarray형태로 준비한다.
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
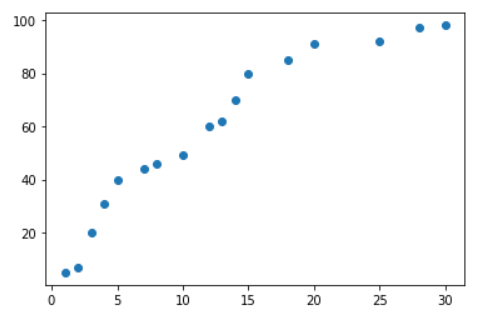
x_data = np.array([1,2,3,4,5,7,8,10,12,13,14,15,18,20,25,28,30]).reshape(-1,1)
t_data = np.array([5,7,20,31,40,44,46,49,60,62,70,80,85,91,92,97,98]).reshape(-1,1)
plt.scatter(x_data.ravel(),t_data.ravel())
plt.show()
2. Linear Regression model 정의
y = Wx + b 와 같이 Linear regression model( Hypothesis )을 정의한다. 여기서 W는 weight이고 b는 bias를 의미한다. 이 예제에서는 랜덤값을 사용한다.
W = np.random.rand(1,1)
b = np.random.rand(1)
## 주의해야 할 점은 W와 같은 경우 Multiple Linear Regression 고려해 nx1 꼴로 만들어주는게 효율적이다.
H = np.dot(x_data, W) + b
3. loss function 정의
loss function(손실함수)는 cost function 이라고도 불린다.
def loss_func(x, t):
y = np.dot(x,W) + b # y = XW + b
return np.mean(np.power(t-y,2)) # 최소제곱법
4. Learning rate 정의
learning rate를 정의한다. 일반적으로 초기에는
1e-4정도로 설정하고 loss 값을 확인하고 수치를 조절한다.
learning_rate = 1e-4
5. 학습 진행
Gradient Descent method를 이용해서 W와 b를 update 하는 방식으로 구현한다.
f = lambda x : loss_func(x_data, t_data)
for step in range(30000):
W = W - learning_rate * numerical_derivative(f,W)
b = b - learning_rate * numerical_derivative(f,b)
if step % 3000 == 0 :
print('W : {}, b : {}, loss : {}'.format(W,b,loss_func(x_data,t_data)))
W : [[0.27795254]], b : [0.46235041], loss : 3615.5725693594673
W : [[3.92221962]], b : [3.52920071], loss : 146.34608793662366
W : [[3.79606552]], b : [5.89354627], loss : 127.60313828483086
W : [[3.69227693]], b : [7.83872359], loss : 114.91685419386076
W : [[3.60688873]], b : [9.43904584], loss : 106.33006251890744
W : [[3.53663876]], b : [10.75565142], loss : 100.51803823028591
W : [[3.47884322]], b : [11.83883966], loss : 96.58413280783454
W : [[3.43129408]], b : [12.72999248], loss : 93.92144402605456
W : [[3.3921748]], b : [13.4631553], loss : 92.11918627268237
W : [[3.35999087]], b : [14.06633772], loss : 90.89931670632278
6. 예측
학습을 통해 얻어낸
W와b를 가지고 예측을 할 수 있다.
def predict(x):
return np.dot(x,W) + b
print(predict(30))
## [[114.53841039]]
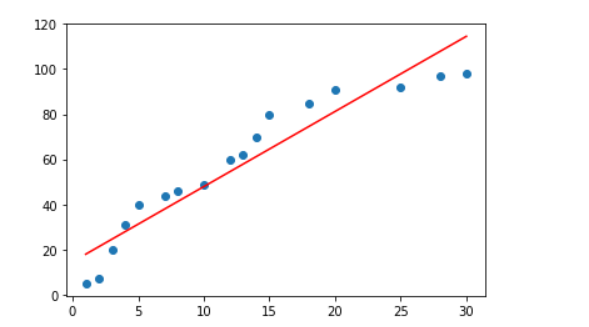
7. 그래프로 확인
학습을 통해 얻어낸
W와b를 가지고 직선 그래프를 그려본다.
plt.plot(x_data,np.dot(x_data,W)+b,'r')
plt.show()