[머신러닝] Logistic Regression 1
Logistic Regression 쉬운 예제(1)(python구현)
Logistic Regression의 쉬운 예제를 통해 구현을 해본다.
Training Data Set
공부시간과 합격에 관한 아주 작은 Data Set을 만든다.
| 시간 | 2 | 4 | 6 | 8 | 10 | 12 | 14 | 16 | 18 | 20 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 합격여부 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
Python code
numpy와pandas를 이용해 구현한다.
0. 수치미분
import numpy as np
def numerical_derivative(f,x):
h = 1e-4
derivative_x = np.zeros_like(x) # 미분한 결과를 저장하는 ndarray
# iterator를 입력변수 x에 대해 편미분을 수행
it = np.nditer(x, flags=['multi_index'])
while not it.finished:
idx = it.multi_index
tmp =x[idx]
x[idx] = tmp + h
fx_plus_h = f(x) # f(x + h)
x[idx] = tmp - h
fx_minus_h = f(x) # f(x - h)
derivative_x[idx] = (fx_plus_h - fx_minus_h)/(2*h)
x[idx] = tmp
it.iternext()
return derivative_x
1. Training data 및 Library
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
x_data = np.arange(2, 21, 2).reshape(-1,1)
t_data = np.array([0,0,0,0,0,0,1,1,1,1]).reshape(-1,1)
2. Weight 및 Bias
input_var = np.random.rand(2,1) # W, b 모두 포함하게 만든다.
3. Loss Function
def loss(input_var):
A = np.concatenate([x_data, np.ones_like(x_data), axis=1)
z = np.dot(A,input_var)
y = 1/(1+np.exp(-z))
delta = 1e-7 # 로그 연산시 무한대로 발산하는것을 방지한다.
# cross entropy
return -np.sum( t_data*np.log(y+delta) + (1-t_data)*np.log(1-y+delta))
4. Learning process
learning_rate = 1e-4
for step in range(30000):
input_var -= learning_rate*numerical_derivative(loss, input_var)
if stage%3000 == 0:
print('W : {}, b : {}, loss : {}'.format(input_var[0],input_var[1], loss(input_var)))
## 결과
W : [0.98832513], b:[0.54972081], loss : 44.869531753345434
W : [0.04402015], b:[-0.13461262], loss : 6.453814777928654
W : [0.08159956], b:[-0.64914488], loss : 5.564879557034531
W : [0.1141694], b:[-1.09157614], loss : 4.9077073635929995
W : [0.14261162], b:[-1.47609988], loss : 4.411418723694001
W : [0.16771556], b:[-1.8145136], loss : 4.027108596702506
W : [0.19012277], b:[-2.11603215], loss : 3.722091077583651
W : [0.21033534], b:[-2.38770113], loss : 3.47451776539932
W : [0.22874206], b:[-2.6348987], loss : 3.2695649058908196
W : [0.2456447], b:[-2.86176157], loss : 3.096962629227913
5. Prediction
def logistic_predict(x)
A = np.concatenate([x, np.ones_like(x)],axis=1)
y = A * input_var # y= wx+b
Z = 1/(1+np.exp(-y))
if z >= 0.5:
result = 1
else:
result = 0
return z, result
study_hour = np.array([[13]])
result = logistic_predict(study_hour)
print('공부시간 : {}, 결과 : {}'.format(study_hour,result))
######### python 결과값 ##########
공부시간 : [[13]], 결과 : (array([[0.58057319]]), 1)
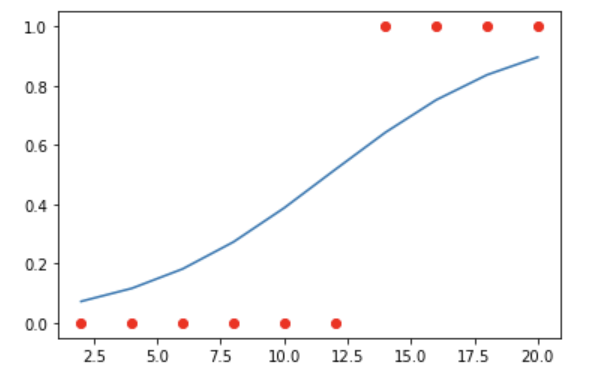
6. 그림으로 확인
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
A = np.concatenate([x_data, np.ones_like(x_data)],axis=1)
z = np.dot(A,input_var)
y = 1/(1+np.exp(-z))
plt.plot(x_data, y)
plt.scatter(x_data, t_data, color='red')
plt.show()