[머신러닝] Tensorflow
Tensorflow 기초
제일 먼저 Tensorflow를 이용한 Linear Regression 구현에 목표를 둔다.
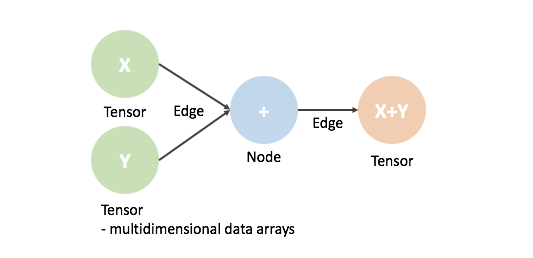
Tensorflow는 graph를 그려주는 library로 이해 할 수 있다. 이 graph는 다음과 같이 구성되어 있다.
- Tensor : 다차원 배열(데이터)
- node : 수식연산(+, -, x, /) , 데이터의 입출력
- Edge : node 와 node를 연결하는 선이다. 이 edge를 따라서 Tensor가 이동한다.
Tensorflow의 설치
Tensorflow에는 1.x 버전과 2.x의 버전이 존재한다. 2.x 의 경우는
keras를 이용한 Tensorflow 버전이다. Tensorflow는 2.x 의 버전이 더욱 간단하고 쉽지만 1.x 버전에 대해서 익히고 2.x버전으로 넘어가도록 한다.
(data_env) C:\Users\User>pip install tensorflow==1.15
tensorflow를 설치할 때 tensorflow==1.15와 같이 버전을 함께 입력해준다.
Tensorflow의 실행
tensorflow의Session을 이용해node를 실행할 수 있다. 가장 기본적인 Hello World 출력 예제와 간단한 덧셈 연산 예제를 살펴본다.
- Hello World 출력
import tensorflow as tf
node = tf.constant('Hello World')
sess = tf.Session()
print(sess.run(node))
## b'Hello World'
print(sess.run(node).decode())
## Hello World
- 10+20 덧셈 연산
import tensorflow as tf
node1 = tf.constant(10, dtype = float32)
node2 = tf.constant(20, dtype = float32)
node3 = node1 + node2
sess = tf.Session()
print(sess.run(node3))
## 30.0
placeholder 사용
scalar 형태의 값 1개를 실수로 받아들일 수 있는 공간이다. 위와 같이 10+20 덧셈 연산 예제를 통해 살펴본다.
import tensorflow as tf
node1 = tf.placeholder(dtype = tf.float32)
node2 = tf.placeholder(dtype = tf.float32)
node3 = node1 + node2
sess = tf.Session()
print(sess.run(node3, feed_dict={node1:10, node2:20}))
## 30.0
Tensorflow 함수
Tensorflow의 함수들에 대해서 알아본다.
1. reduce_mean
평균을 계산하는 함수이다.
import tensorflow as tf
node = tf.constant([[2., 3.], [4., 4.]])
sess = tf.Session()
print(sess.run(node))
## [[2. 3.]
## [4. 4.]]
print(sess.run(tf.reduce_mean(node))) # 3.25
print(sess.run(tf.reduce_mean(node, 0))) # [3. 3.5]
print(sess.run(tf.reduce_mean(node, 1))) # [2.5 4. ]
2. square
성분들을 각각 제곱 해준다.
import tensorflow as tf
node1 = tf.constant([1, 2, 3, 4]) # [1 2 3 4]
node2 = tf.square(node1)
sess = tf.Session()
print(sess.run(node2))
## [ 1 4 9 16]
3. matmul
matrix 곱을 해준다.
import tensorflow as tf
A = tf.constant([[-1, 1],[1, 2]])
B = tf.constant([[1, 2, 3], [4, 5, 6]])
C = tf.matmul(A,B)
sess = tf.Session()
print(sess.run(C))
## [[ 3 3 3]
## [ 9 12 15]]